Understanding MPAN and MPRN Numbers on Energy Meters
When switching your business gas or electricity supplier, you’ll likely need to provide your MPAN (Meter Point Administration Number) for electricity and MPRN (Meter Point Reference Number) for gas. In this article, you’ll learn what these numbers represent, how to find them, and why they’re important when switching or moving business premises.
What is an MPAN number?
An MPAN (Meter Point Administration Number) is a unique number assigned to the electricity meter for a property so the meter can be referenced and identified. It does not change when switching suppliers. Also known as a “Supply Number” or “S Number,” it is typically a 21-digit code that begins with the letter ‘S’. The MPAN helps make sure that the correct meter is billed, making it essential for accurate energy management and billing.
Example of MPAN number on your bill:
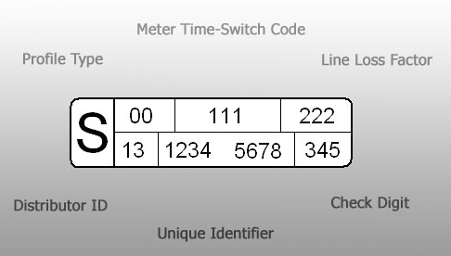
What do the numbers on an MPAN mean?
Each of the numbers in your MPAN has a meaning. The first two numbers shown as ‘00’ in the above example, represent your meter’s profile class, showing typical electricity usage. For example, Profile Class 1 covers domestic unrestricted customers, while higher classes relate to non-domestic maximum demand customers based on their electricity usage patterns and peak load factors. The different classes are listed below:
- Profile Class 1: Domestic customers with unrestricted usage.
- Profile Class 2: Domestic Economy 7 users with off-peak tariffs.
- Profile Class 3: Non-domestic customers with unrestricted usage.
- Profile Class 4: Non-domestic Economy 7 users.
- Profile Class 5: Non-domestic maximum demand with less than 20% peak load factor.
- Profile Class 6: Non-domestic maximum demand with a 20-30% peak load factor.
- Profile Class 7: Non-domestic maximum demand with a 30-40% peak load factor.
- Profile Class 8: Non-domestic maximum demand over 40%.
- Profile Class 00: High peak usage above 100 kW.
The Peak Load Factor is a ratio that measures how efficiently your business uses electricity. It is calculated by dividing the actual electricity consumption (in kWh) during a specific period by the maximum potential usage at your peak demand level during that same period. Essentially, it reflects how much of your available energy capacity is utilized over time. A lower peak load factor indicates less efficient energy usage, while a higher factor shows more consistent energy use across the period. Ofgem’s P272 regulation requires meters with S numbers between 05 and 08 to be switched to half-hourly meters automatically.
Meter Time Switch Code (MTC)
The next three digits (shown as 111) on the MPAN indicate whether your meter is a single-rate or time-of-use meter. While most businesses have single-rate meters, some benefit from tariffs that offer different rates based on the time of day, such as day/night or weekend rates.
Line Loss Factor (LLF)
LLF is represented by the next three digits (shown as 222) in the MPAN and relates to the Distribution Use of System (DUoS) charges. This reflects the amount of electricity lost as it travels to your meter. Electricity loss happens due to resistance in the wires, meaning the further your property is from a distribution centre, the more energy is lost during transmission. A bigger distance results in greater resistance and higher costs, as more energy is needed to cover the distance. If you also factor in metering inaccuracies, unmetered fixtures such as street lighting and theft, an average of about 7% of electricity is lost in this process.
Distribution ID
The next two digits (shown as 13) of the MPAN indicate the regional distribution company responsible for managing the electricity supply to your property. This Distribution ID helps you identify which company operates the local network. Here is a list of Distribution IDs and which companies they represent:
| ID | Name | Operator |
| 10 | Eastern England | UK Power Networks |
| 11 | East Midlands | Western Power Distribution |
| 12 | London | UK Power Networks |
| 13 | Merseyside and Northern Wales | ScottishPower |
| 14 | West Midlands | Western Power Distribution |
| 15 | North Eastern England | Northern Power Grid |
| 16 | North Western England | Electricity North West |
| 17 | Northern Scotland | SSE Power Distribution |
| 18 | Southern Scotland | ScottishPower |
| 19 | South Eastern England | UK Power Networks |
| 20 | Southern England | SSE Power Distribution |
| 21 | Southern Wales | Western Power Distribution |
| 22 | South Western England | Western Power Distribution |
| 23 | Yorkshire | Northern Power Grid |
| 27 | Unmetered Supply | Unmetered Supply |
Meter Point ID
Following this, the Meter Point ID, an eight-digit number (shown as 1234 5678), is unique to your meter within your distribution area.
Check Digit
Lastly, the final three digits (shown as 345), known as the Check Digit, are calculated using the Distributor ID and Meter Point ID to ensure accuracy in identifying your meter.
How to find your MPAN number
Your MPAN number is usually found on your electricity bill, often displayed in the top left or bottom right corner. It’s not printed on your electricity meter itself. If you don’t have access to a bill, you can contact your regional electricity distribution company to retrieve your MPAN. Or, you can use online tools provided by energy networks to locate your MPAN based on your property’s address. Having this number is essential when switching suppliers or managing your electricity account.
What is an MPRN number?
An MPRN (Meter Point Reference Number) is a unique identifier for your gas supply point. This number, typically between 6 and 10 digits, helps gas suppliers locate and manage the gas supply to your property. As with the MPAN number , the MPRN is specific to the physical location of the gas meter and does not change when you switch gas suppliers. You can usually find it on your gas bill or directly on the meter itself. It makes sure you are accurately charged for your gas usage.
Is my gas meter serial number the same as MPRN?
No, your gas meter serial number (MSN) is not the same as your MPRN. The MSN is a unique identifier for the physical gas meter itself, consisting of letters and numbers, and is typically found on the meter box where as the MPRN (Meter Point Reference Number) identifies the gas supply point to your property.
Why do you need to know your energy meter numbers?
Knowing your MPAN and MPRN numbers is essential when switching energy suppliers or moving to a new business premises. Without them, it can be difficult to switch providers, set up new energy services, or resolve any billing issues. Additionally, having these numbers on hand simplifies communication with suppliers and helps avoid any mix-ups with your energy supply.
Does my MPAN and MPRN change with a new meter?
No, your MPAN and MPRN numbers remain the same even if you get a new meter installed as these numbers are tied to the location of the electricity or gas supply point, not the meter itself. The only time your MPAN or MPRN would change is if you move to a new property. If you install additional meters at a different location, you’ll receive new MPAN or MPRN numbers for that site, but your original meter’s numbers will stay the same.
Will your MPAN and MPRN change if you switch suppliers?
No, your MPAN and MPRN numbers will not change when you switch energy suppliers due to the fact these numbers are specific to the electricity and gas supply points at your property, not to the supplier. Switching suppliers only changes the company providing your energy, but the MPAN and MPRN remain the same. This means that the energy supply points stay correctly identified regardless of which supplier you choose.
What is an Independent Gas Transporter (IGT)?
An Independent Gas Transporter (IGT) is a company that manages gas pipelines for properties not connected to the National Grid, often in rural or new developments. IGTs operate smaller networks compared to the National Grid. While Ofgem regulates their charges, gas supplied through an IGT can sometimes be more expensive due to the additional infrastructure costs involved in managing their independent pipelines.
Professional Energy Services has a range of energy metering services and can specific a bespoke energy contract to your needs to maximise the benefits to your business with the right metering solution for you. Contact us to find out more.
Related Posts

Everything you need to know about your Business Energy Bill

Non-Commodity Electricity Charges – DUoS and TNUoS Explained
